From Intracellular Signaling to Population Oscillations: Bridging Size and Time Scales in Collective Behavior
Allyson E. Sgro, David J. Schwab, Javad Noorbakhsh, Troy Mestler, Pankaj Mehta, and Thomas Gregor. Molecular Systems Biology 11: 799 (2015). 
Abstract
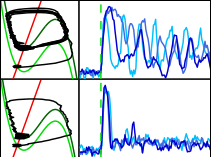
Collective behavior in cellular populations is coordinated by biochemical signaling networks within individual cells. Connecting the dynamics of these intracellular networks to the population phenomena they control poses a considerable challenge because of network complexity and our limited knowledge of kinetic parameters. However, from physical systems we know that behavioral changes in the individual constituents of a collectively-behaving system occur in a limited number of well-defined classes, and these can be described using simple models. Here we apply such an approach to the emergence of collective oscillations in cellular populations of the social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum. Through direct tests of our model with quantitative in vivo measurements of single-cell and population signaling dynamics, we show how a simple model can effectively describe a complex molecular signaling network and its effects at multiple size and temporal scales. The model predicts novel noise-driven single-cell and population-level signaling phenomena that we then experimentally observe. Our results suggest that like physical systems, collective behavior in biology may be universal and described using simple mathematical models.
Summary
Collective behavior in cellular populations is coordinated by biochemical signaling networks within individual cells. In this study, we developed a model based on experimental data linking single-cell signaling dynamics to population-level behaviors in Dictyostelium.
Highlights
- Single Dictyostelium cells are well described as excitable, oscillatory systems
- A universal, top-down model reproduces single cell and population-level behaviors
- Model-based predictions were validated in individual cells and in cellular populations
- Stochasticity drives the emergence and continued coordination of collective behavior